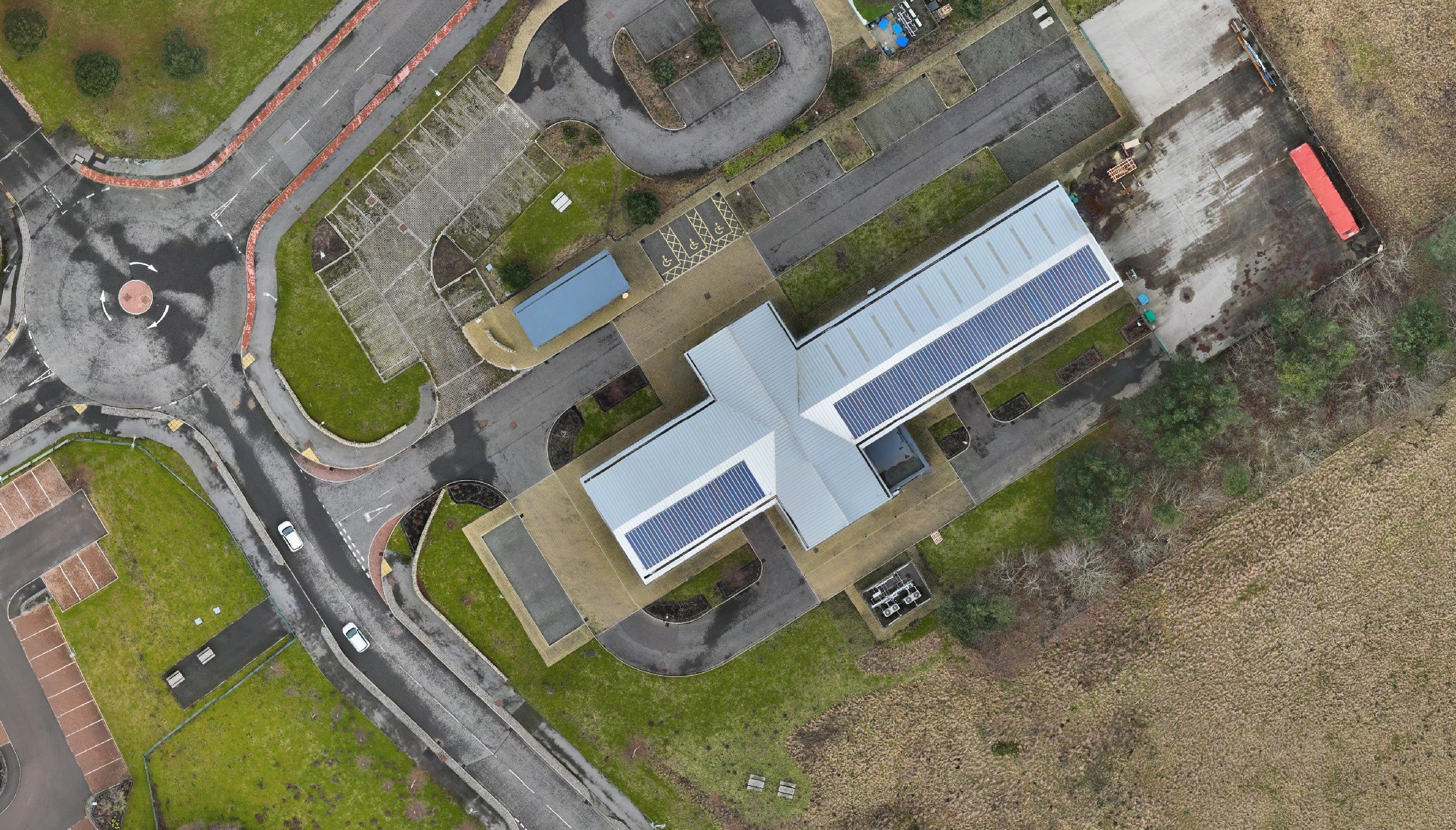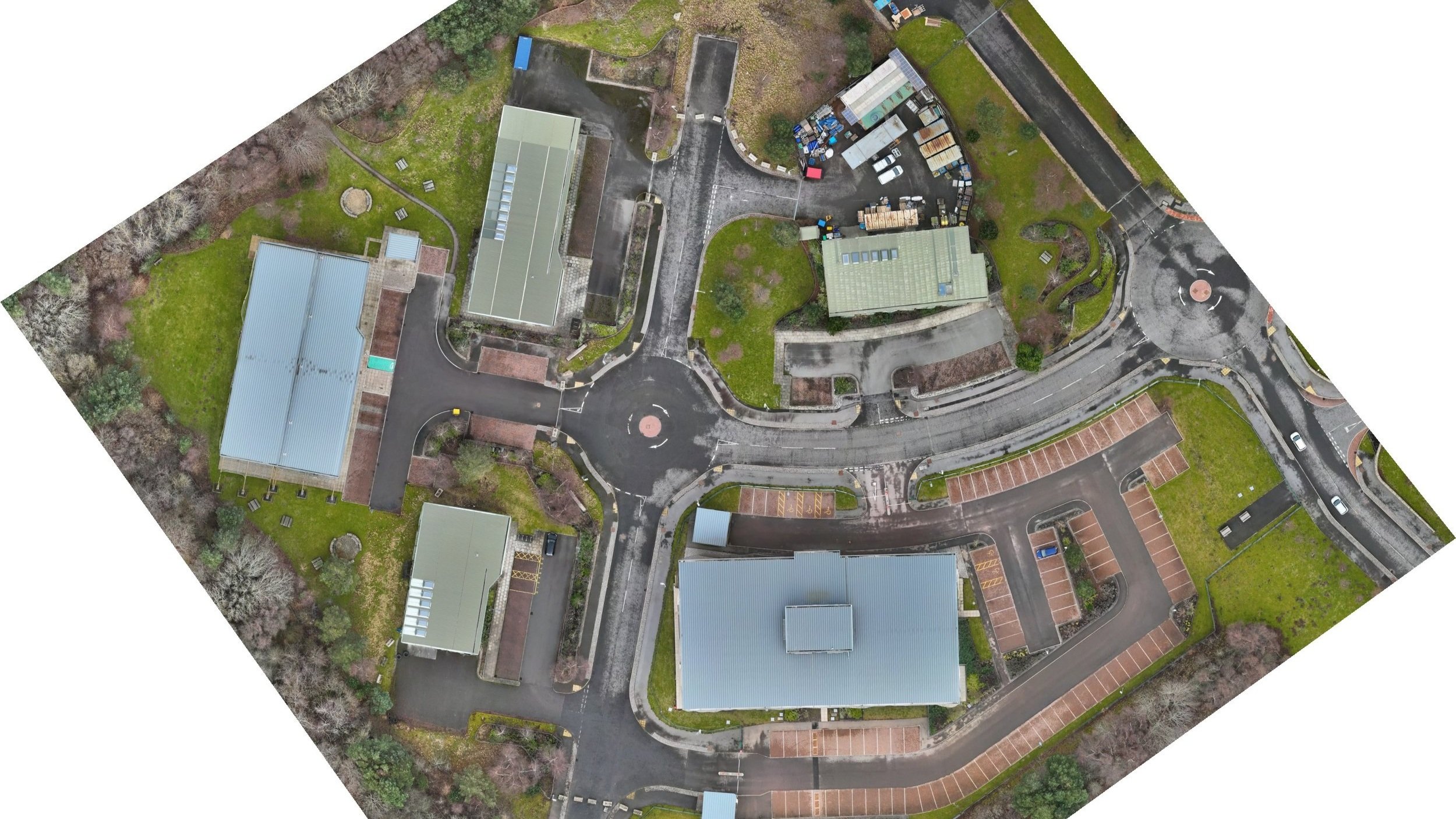
High Resolution Drone Topographical and Mapping Services
Topographical surveys are essential for various construction projects, including the construction of buildings, roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. Today the use of drones for topographical surveys has become increasingly popular.
Whatever you project requirements are:
Site pre-condition surveys.
Planning consent surveys.
and much more
If you would like to explore the use of drones and Aerial Mapping / Surveys for topographical mapping and how PB Aerial Imaging drone mapping solutions can help your project contact us today.
Why Choose PB Aerial Imaging’s Aerial Mapping Services?
Whether it be high resolution and accurate GeoTiffs, Point Clouds, DSM,DEM, or DTMs, Full Line works, Contours or spot heights,
Vast Experience from peatland restoration to coastal erosion monitoring, construction site mapping, Pre Start Site surveys, housing development design to volumetric calculations.
We work closely with you to identify your exact requirements.
Our in house processing team can provide you with a dataset that can be used throughout and beyond the project life and accurately repeated time after time. Obviously we can always just supply you with the raw captured data if you wish to process it yourself.
Our fleet of drones can map huge areas much quicker than traditional surveys providing accurate data at very high resolution.
We install our own GCPs or can utilise your pre installed fixed ground control points. As all our kit is the latest multi band L1/L2 and L5 GNSS receivers your Resolution and absolute accuracy is assured by using our fleet of RTK (Real Time Kinematic) enabled Drones and GNSS receivers we can achieve centimetre level accuracy.
We host all our clients' High resolution 3D Models on our secure dedicated web app which can be viewed on any platform with no loss of quality, with the ability to take measurements and add annotations shared throughout the team.
Why use a drone for Aerial Mapping?
Topographical surveys are essential for various construction projects, including the construction of buildings, roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. Traditionally, topographical surveys were carried out using ground-based surveying equipment, such as total stations and GPS receivers. However, the use of drones for topographical surveys has become increasingly popular in recent years. There are several reasons why using a drone for topographical surveys can be advantageous:
Fast and Efficient
Using a drone for topographical surveys can be faster and more efficient than traditional ground-based surveys. Drones can cover large areas quickly and capture high-resolution data in a fraction of the time it would take to do so manually.
Accurate Data
Drones can capture highly accurate data, which is essential for creating precise topographical maps. By using RTK drones Installing Ground Control Points and check points, surveyors can capture data with a level of accuracy that is not possible with ground-based surveys.
Detailed Imagery
Drones can capture high-resolution imagery of the survey area, providing a detailed view of the terrain. This level of detail can be useful for identifying potential issues that may impact the construction project.
Improved Safety
Using drones for topographical surveys can improve safety by reducing the need for surveyors to work in hazardous areas, such as steep slopes or near waterways. Drones can capture data from a safe distance, minimizing the risk of injury to surveyors.
Cost-Effective
Using drones for topographical surveys can be cost-effective compared to traditional survey methods. Drones require less manpower, equipment, time and can cover larger areas, resulting in cost savings for the project.
Real-Time Data
Drones can provide real-time data, which can be particularly useful for monitoring ongoing projects. This can enable project managers to make informed decisions quickly, leading to improved project outcomes.
Drone missions and flight paths can be utilised time after time to reproduce and compare the areas weeks, months even years after the initial survey.
In conclusion, using drones for topographical surveys can offer numerous advantages over traditional survey methods. Drones can provide accurate data, detailed imagery, improved safety, cost savings, and real-time data, making them a valuable tool for construction projects. By using drones for topographical surveys, surveyors can improve efficiency, accuracy, and safety, leading to better project outcomes.
Common Drone Mapping Outputs
Orthomosaic
Basically an orthomosaic is like a giant Google Earth photo, but more detailed and accurate. This large scale zoomable image is an aerial photo that has been corrected for lens distortion, camera tilt, perspective, and topographic relief, which is changes in the elevation of the earth’s surface. Google Maps/Earth can be upto 10 years out of date, with our Orthomosaic photos you have a highly accurate up to date aerial map of your site which can be utilised in a multitude of different ways.
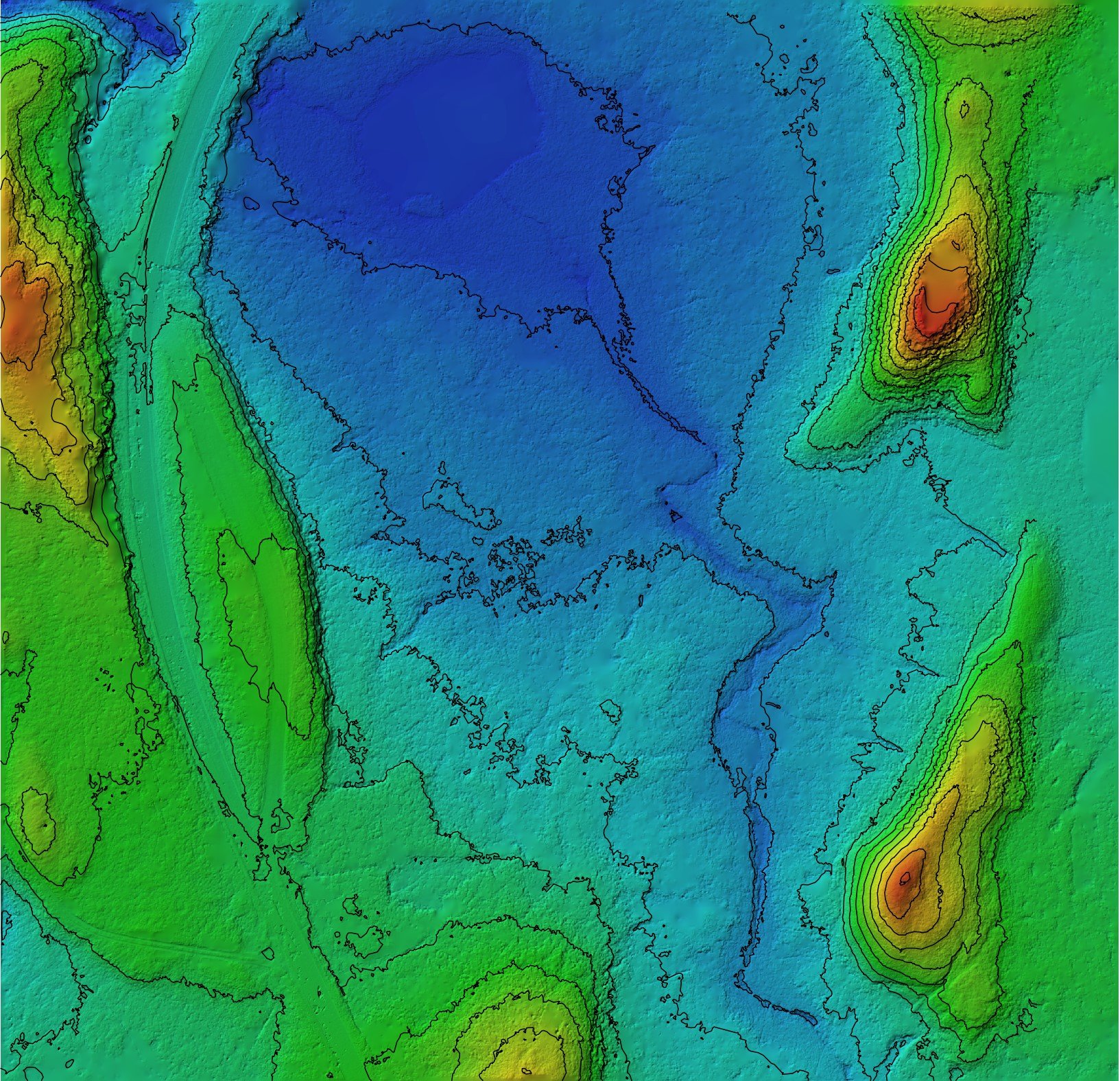
Digital Elevation Models (DEM): are earth (topographic) models of the Earth’s surface. DEM allows you to generate slope (rise and fall in degrees or per cent), aspect (slope direction), and hillshade (grayscale 3D representation of the surface, with the sun's relative position taken into account for shading the image).
Digital Terrain Models (DTM): A 3D representation of a terrain surface. DTMs include contours, as well as features such as rivers, ridge lines, etc.
Digital Surface Models (DSM): Incorporates elevations from natural and built surfaces, such as buildings, tree canopy, and powerlines. Essentially, a DSM represents the earth's surface and all objects on it.
Contours
A contour is a line on a map that connects points of equal elevation, creating a representation of the shape and slope of the land. Contours are commonly used in cartography and topographic maps to visualize the terrain of a specific area.
Tin Surfaces
A Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN) surface is a type of digital surface model used in mapping and surveying. It is created by connecting a set of irregularly spaced data points with a network of triangles, each with its own elevation value. TIN surfaces are used to represent complex terrain and elevation data in a way that is more accurate and visually appealing than other methods. TIN surfaces are commonly used in geospatial applications such as topographic mapping, hydrologic modeling, and land use planning. TIN surfaces can be created using various software programs and can be generated from a variety of data sources, including lidar, photogrammetry, and ground surveying.
3d Models & Fly Throughs
Drones are equipped with cameras or other sensors that can capture high-resolution images and data from multiple angles, which can be processed to create a detailed 3D model. The resulting model can be used to visualize and analyze the object or environment in three dimensions, providing insights into its shape, dimensions, and features. Drone 3D models are commonly used in industries such as construction, architecture, and engineering for site planning, design visualization, and project management.
PDF Output Examples











